what is a 12-Layer PCB?
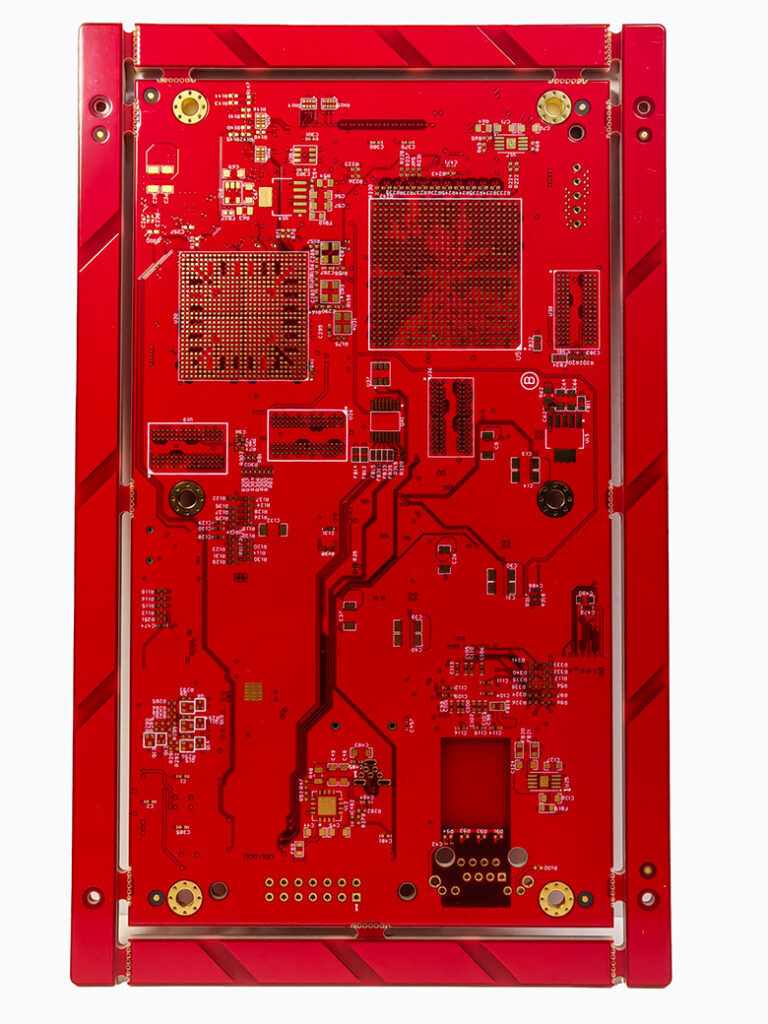
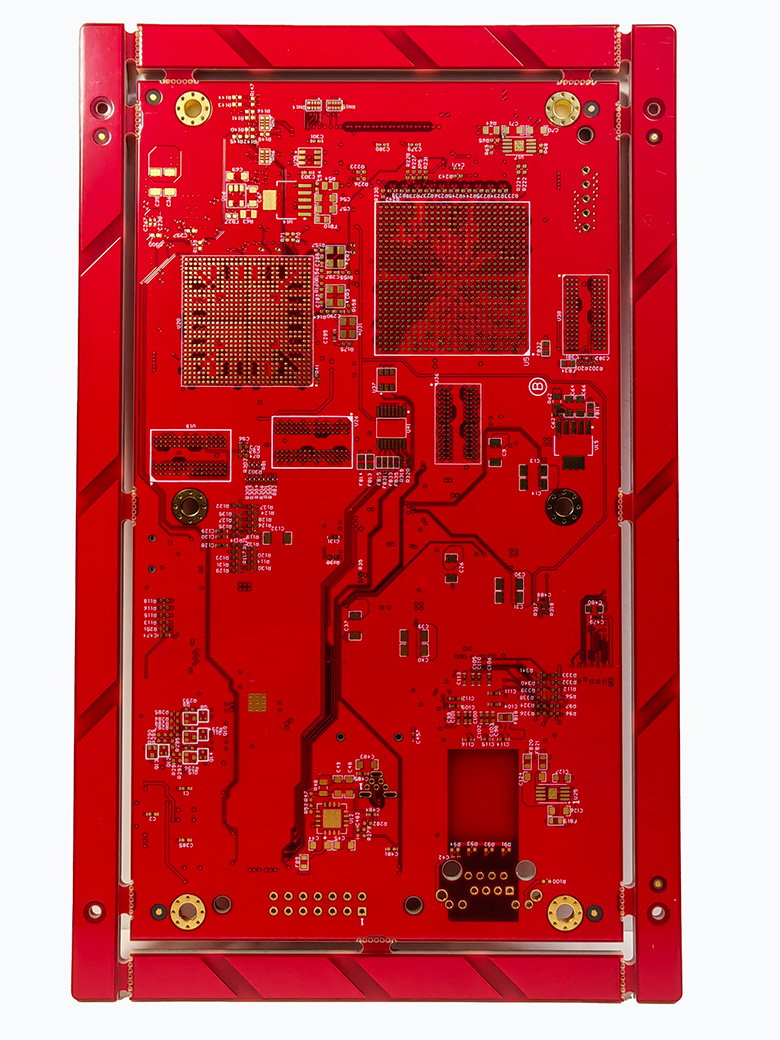
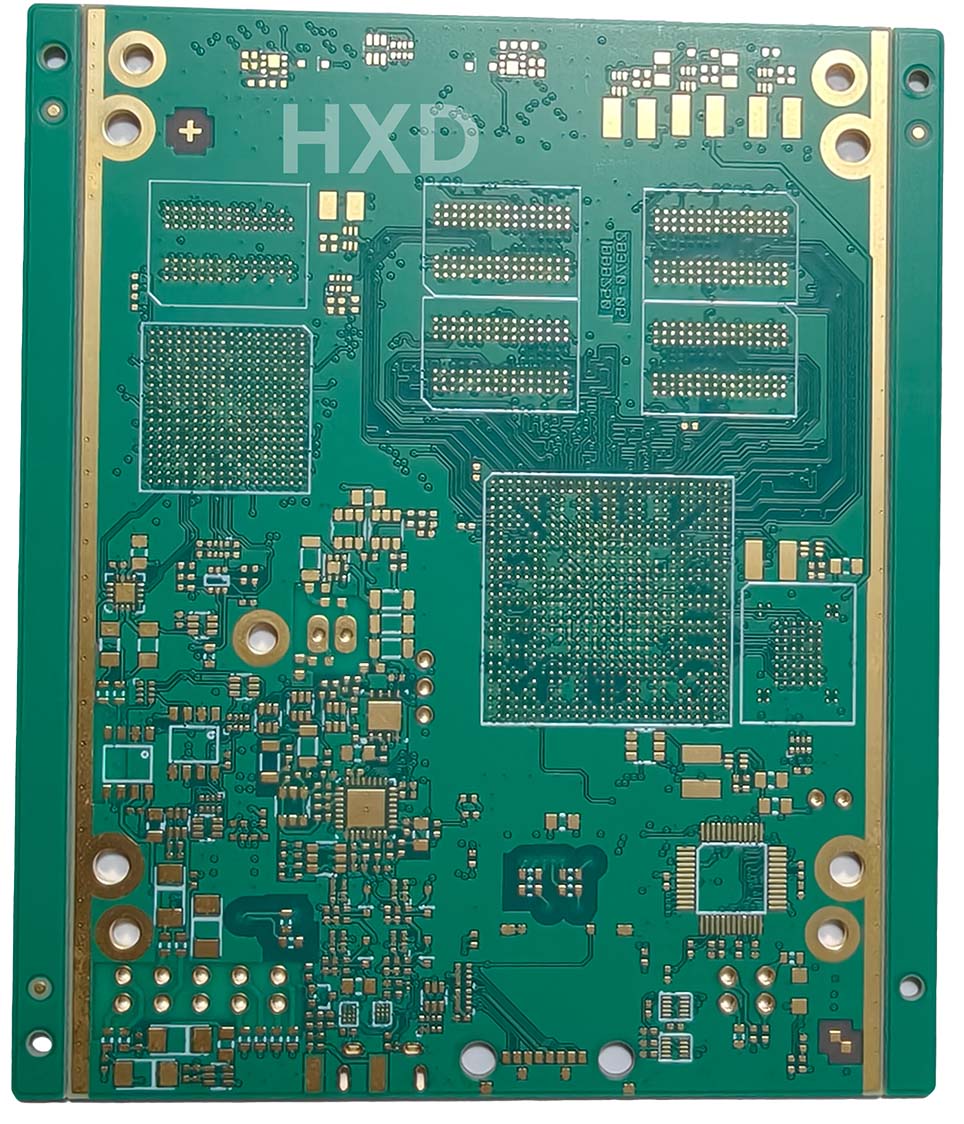
A 12-layer PCB is a multilayer printed circuit board made by stacking and laminating 12 layers of conductive copper foil. Each layer is separated by insulating dielectric materials.
Structure
The board typically consists of 2 outer layers (Top and Bottom) and 10 inner layers. These inner layers are strategically assigned as Signal, Ground, or Power planes to handle complex electrical connections and provide EMI shielding.
Materials
- Copper: The conductive material used to transmit signals and power.
- Prepreg: An insulating material that bonds the cores and copper foils together.
- Core / Substrate: A rigid dielectric material with copper foil that provides structural support and insulation.