When to Use an 8-Layer PCB?
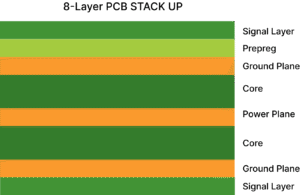
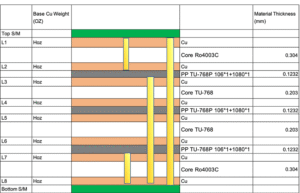
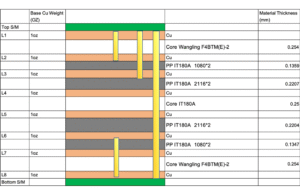
An 8-layer PCB comprises 8 layers of copper, each separated by a layer of insulating material (Prepreg and Core). It is a high-end PCB. Typically, 8-layer PCBs are used for projects with extremely high requirements for signal speed, power handling, and electromagnetic shielding. Specifically, 8-layer PCBs are suitable for the following scenarios:
- High-Density Design:When your product needs to integrate many components and complex routing in a limited area, an 8-layer structure provides enough routing layers to carry these circuits. It is especially suitable for micro-electronics and wearable devices. If your design involves multiple different Power Islands, an 8-layer PCB provides sufficient space for routing and ensures isolation between different subsystems.
- Strict Requirements for Signal Integrity (SI):The stackup of an 8-layer board is symmetrical. This structure effectively controls impedance accuracy and supports the stable transmission of high-speed signals above 28Gbps. In addition, the design usually places signal layers next to ground or power planes. This can reduce crosstalk between signals by over 30% and provide a clear return path.
- High Requirements for EMC/EMI:By adding multiple ground and power planes, an 8-layer PCB acts as a shield for internal signal layers. This structure can significantly reduces Electromagnetic Interference (EMI). If your device needs to operate in environments with strong radiation or complex electromagnetic noise, the 8-layer structure provides powerful anti-interference capability.
- Thermal Management:The dedicated power planes of an 8-layer PCB can handle high current above 10A. When working with high voltage above 500V, the multilayer structure provides better interlayer insulation and creepage distance, reducing the risk of electrical arcing.When your product includes high-power components, such as MOSFETs with power dissipation above 5W and strict thermal requirements, an 8-layer PCB uses large internal copper areas and thermal vias to dissipate heat more effectively.